##TODO…
Introduction
The intention of this vignette is to show how to plot different styles of cost-effectiveness acceptability curves using the BCEA package.
R code
To calculate these in BCEA we use the bcea()
function.
The plot defaults to base R plotting. Type of plot can be set
explicitly using the graph argument.
ceplane.plot(he, graph = "base")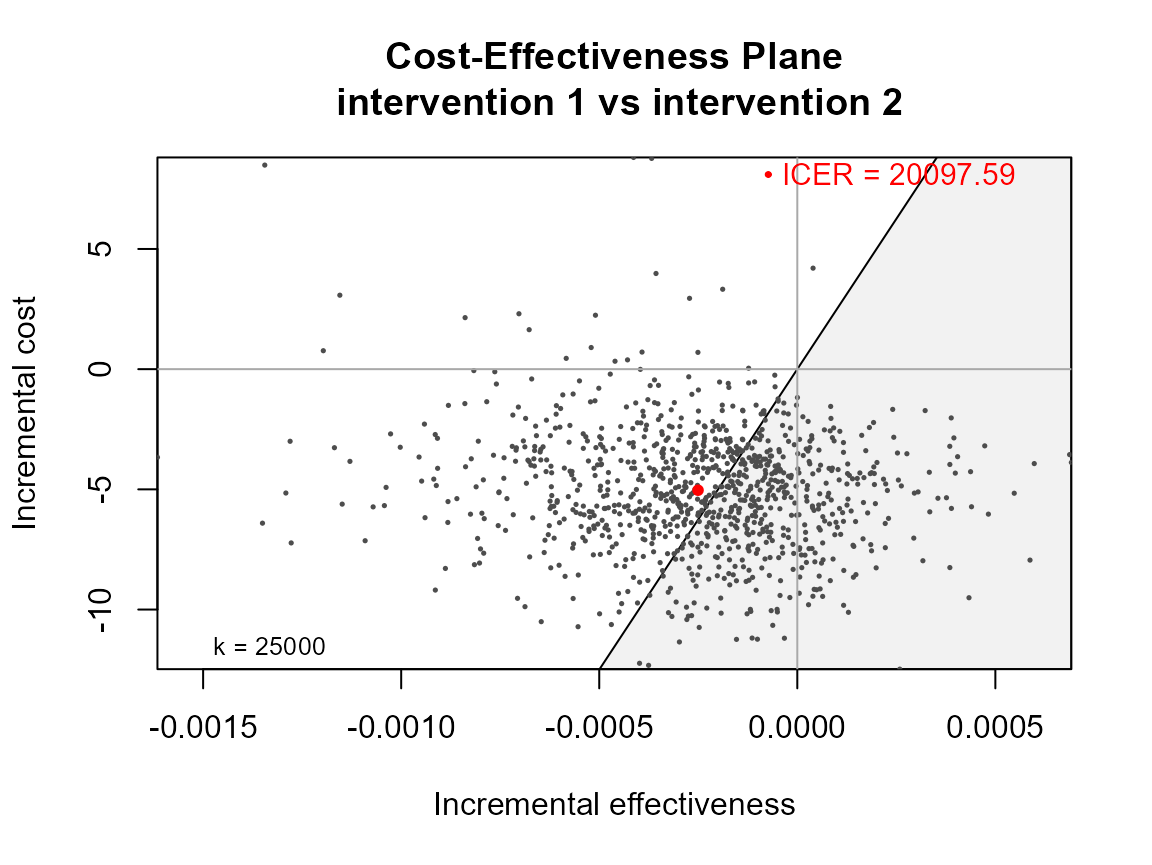
ceplane.plot(he, graph = "ggplot2")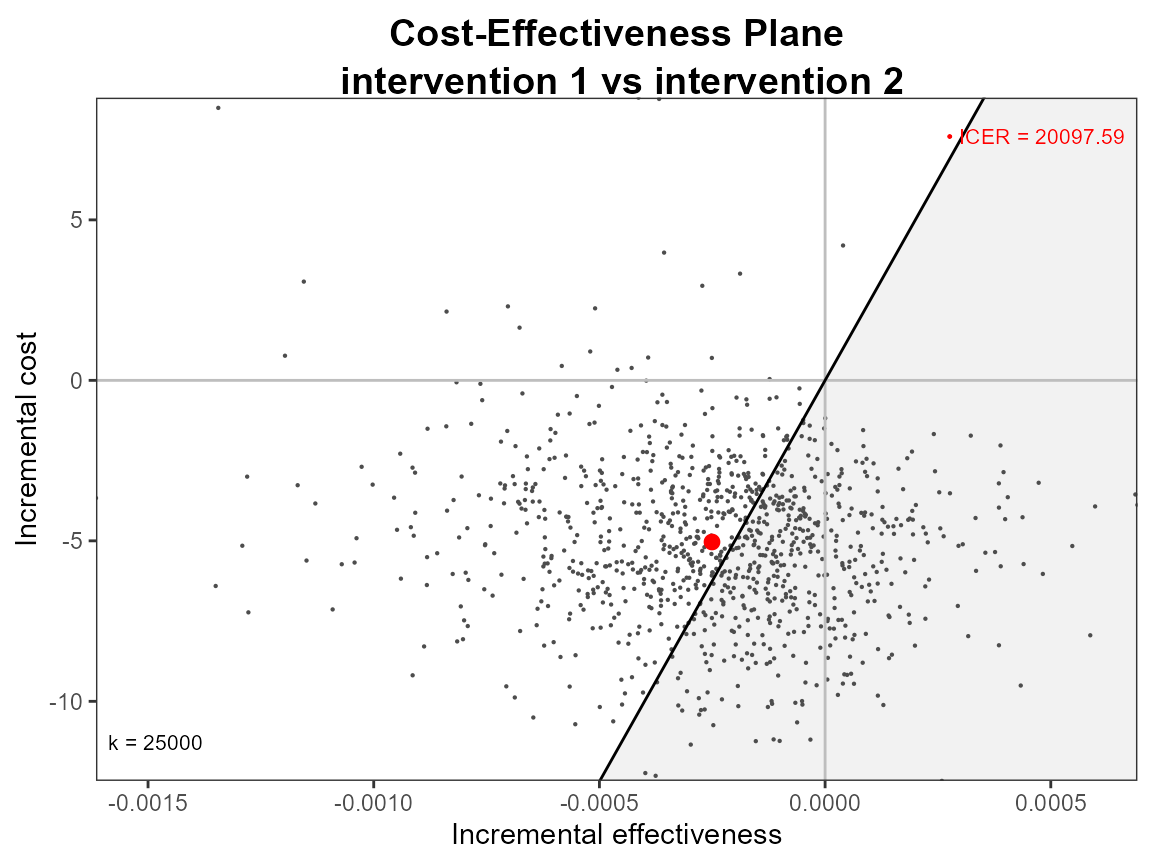
# ceac.plot(he, graph = "plotly")Other plotting arguments can be specified such as title, line colours and theme.
ceplane.plot(he,
graph = "ggplot2",
title = "my title",
line = list(color = "green", size = 3),
point = list(color = "blue", shape = 10, size = 5),
icer = list(color = "orange", size = 5),
area = list(fill = "grey"),
theme = theme_linedraw())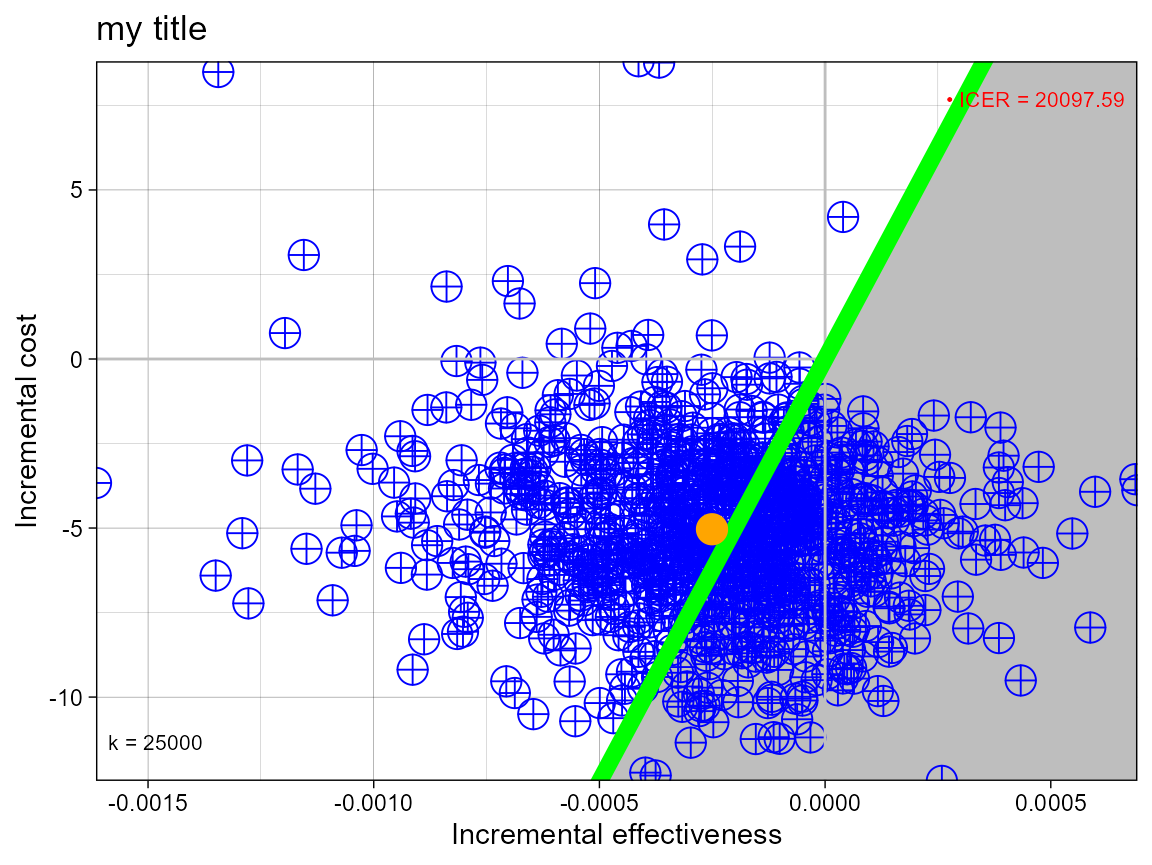
If you only what the mean point then you can suppress the sample
points by passing size NA.
ceplane.plot(he,
graph = "ggplot2",
point = list(size = NA),
icer = list(size = 5))
#> Warning: Removed 1000 rows containing missing values (`geom_point()`).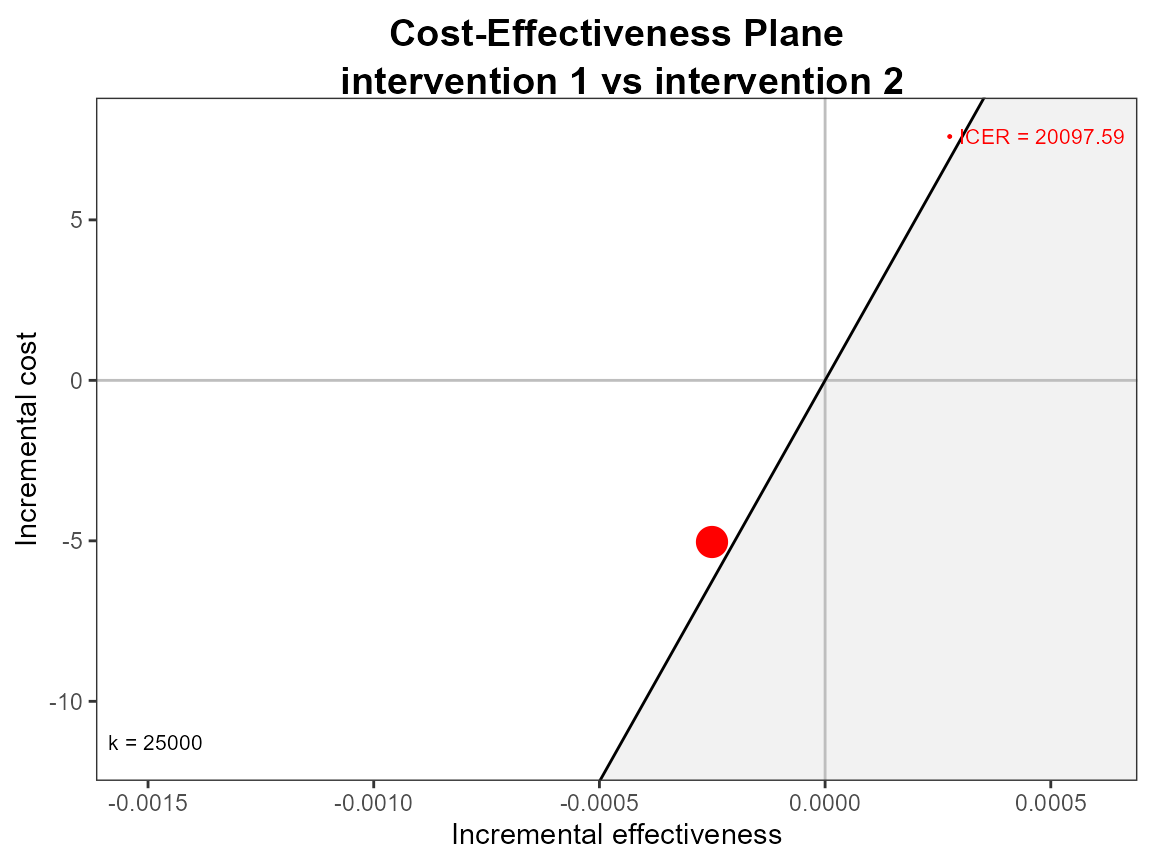
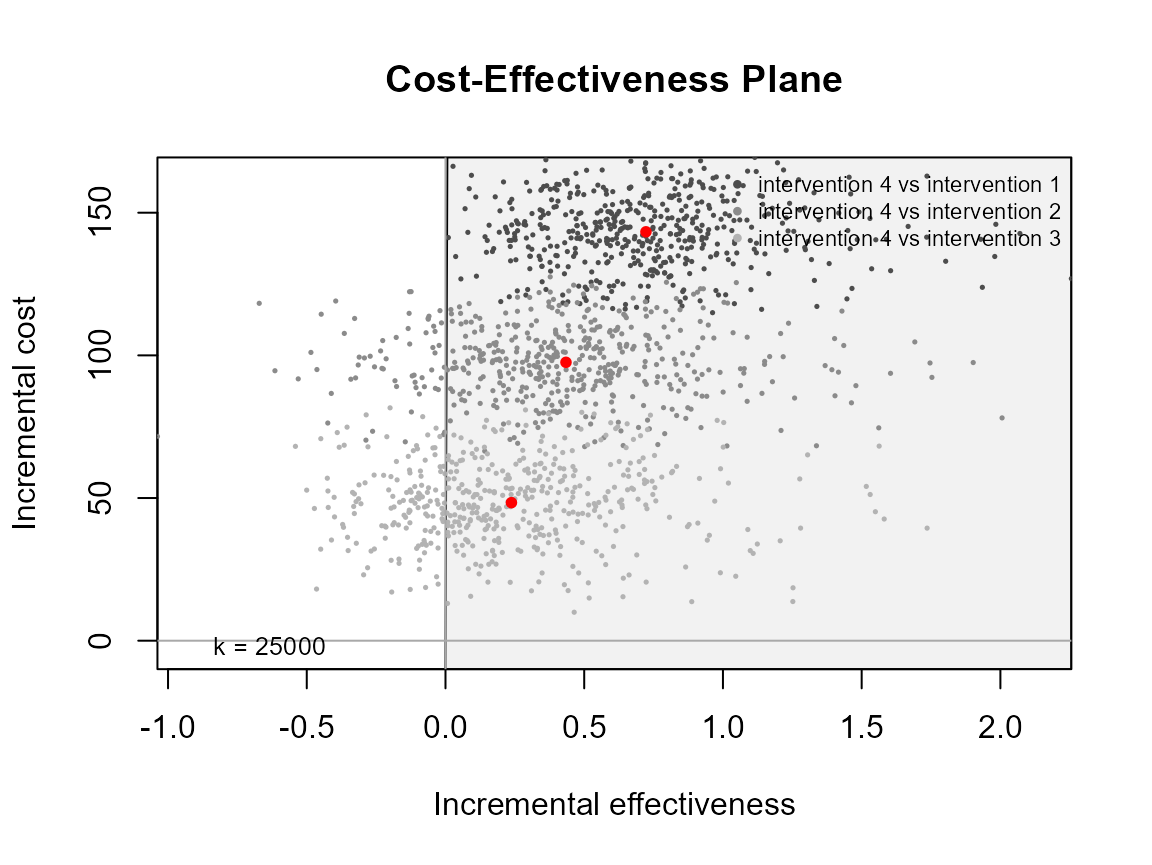
Multiple interventions
This situation is when there are more than two interventions to consider.
R code
ceplane.plot(he)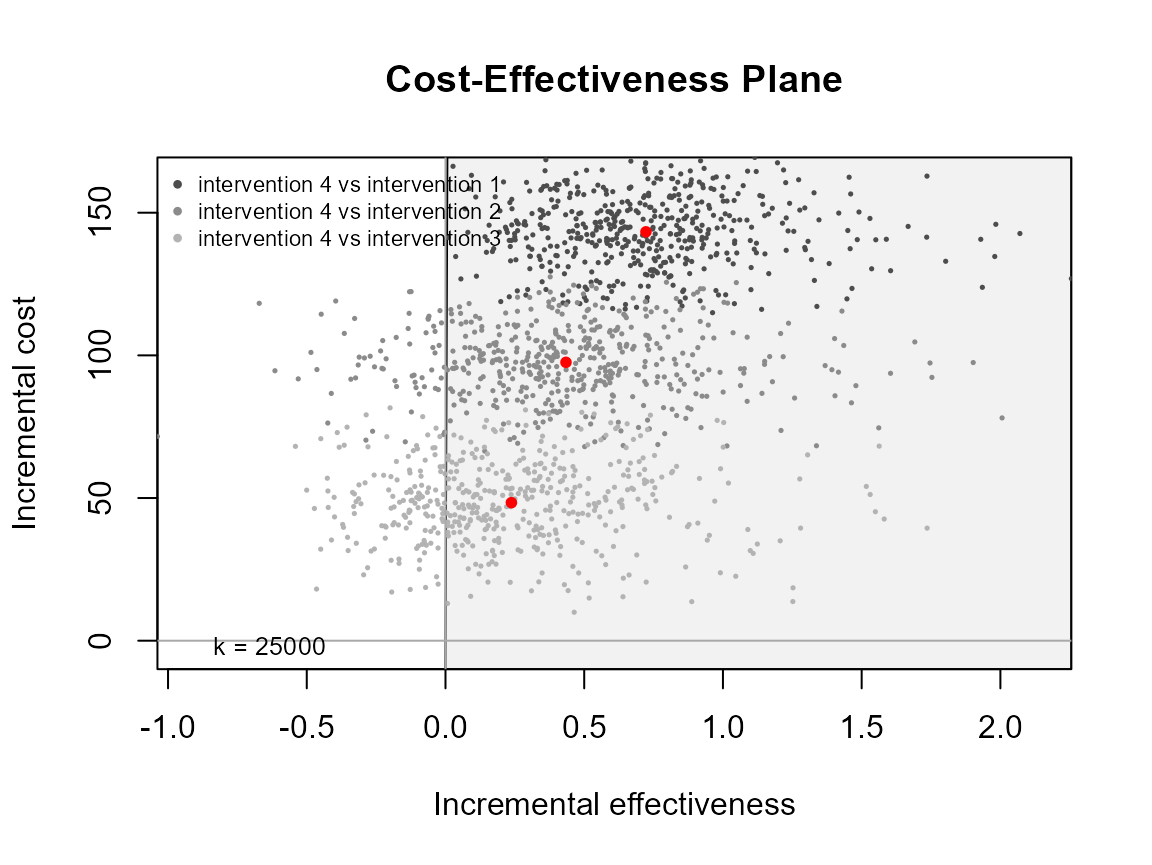
ceplane.plot(he, graph = "ggplot2")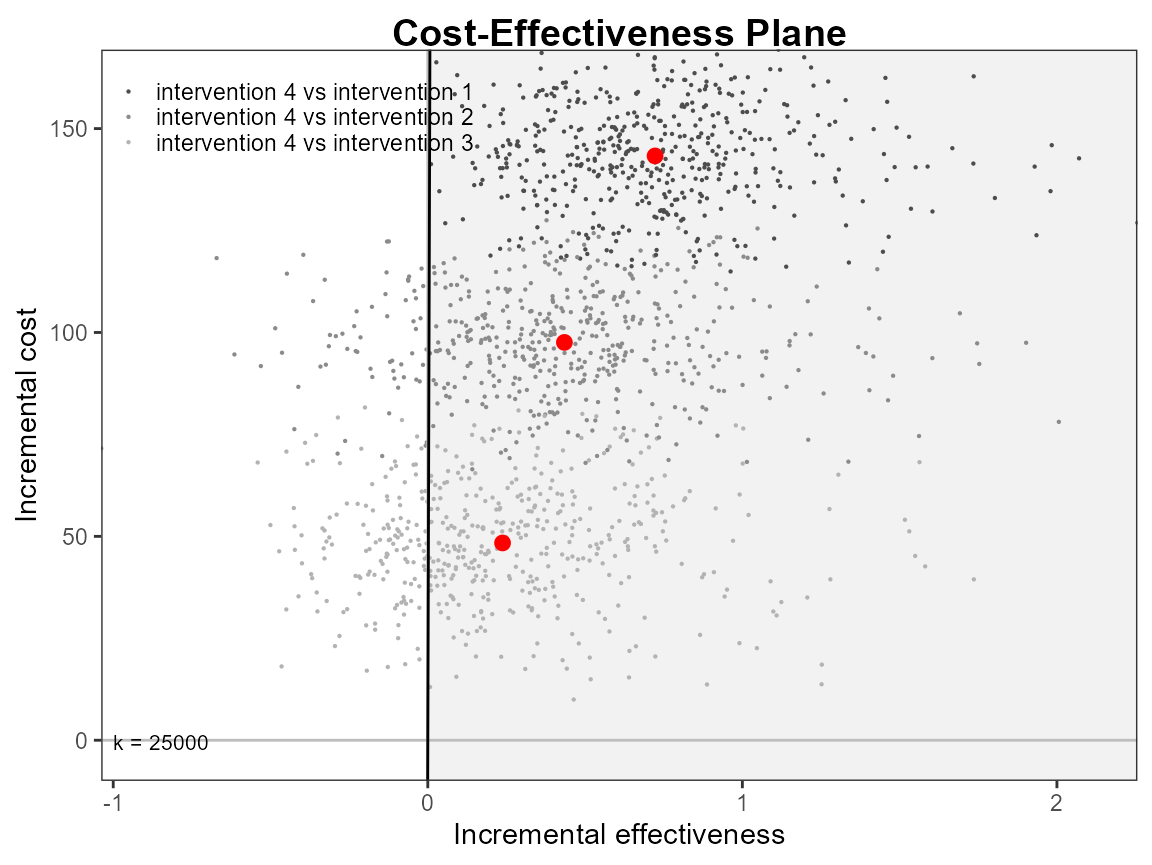
ceplane.plot(he,
graph = "ggplot2",
title = "my title",
line = list(color = "red", size = 1),
point = list(color = c("plum", "tomato", "springgreen"), shape = 3:5, size = 2),
icer = list(color = c("red", "orange", "black"), size = 5))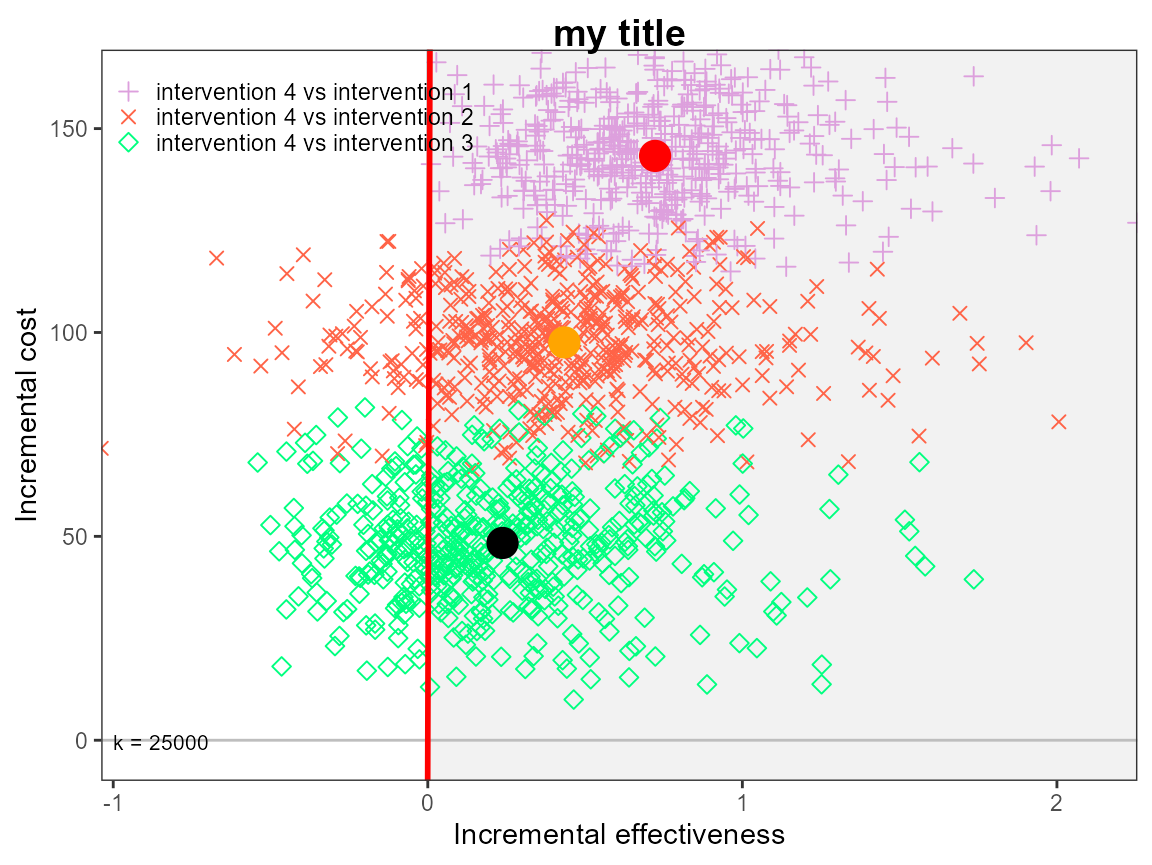
Reposition legend.
ceplane.plot(he, pos = FALSE) # bottom right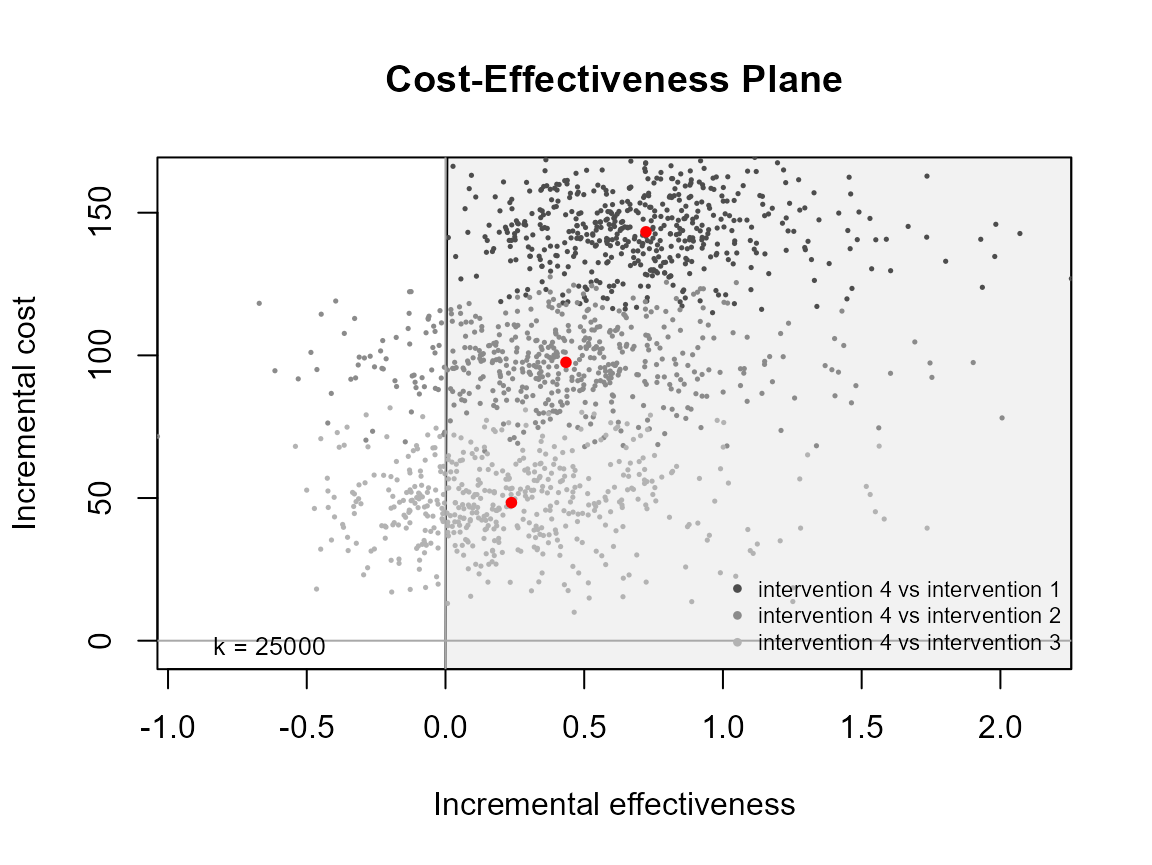
ceplane.plot(he, pos = c(0, 0))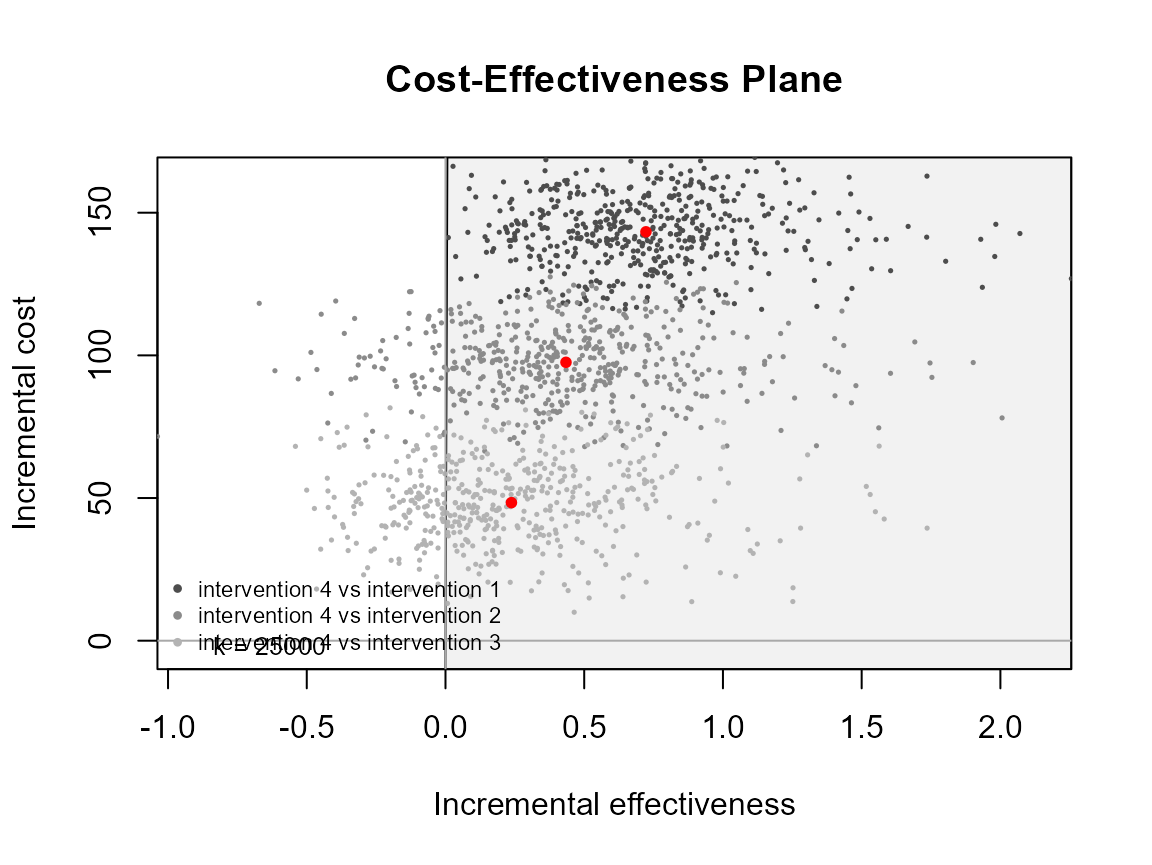
ceplane.plot(he, pos = c(0, 1))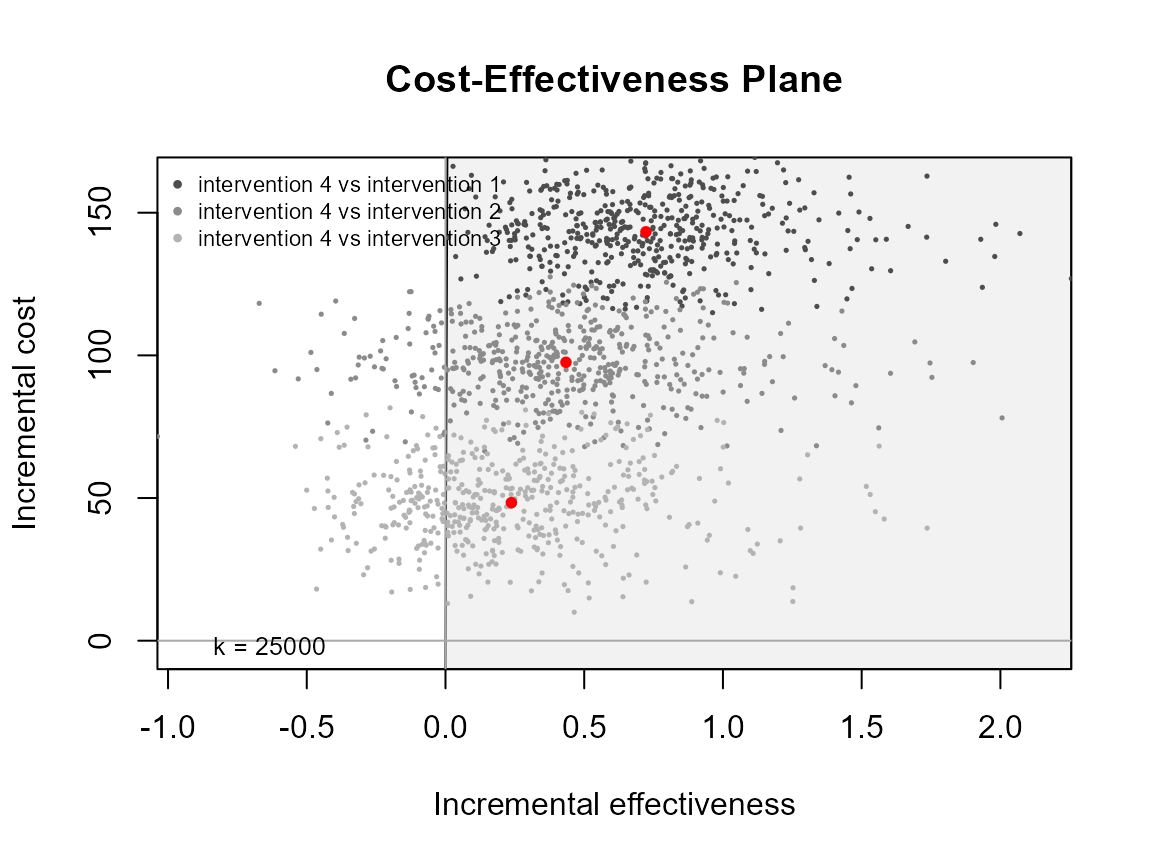
ceplane.plot(he, pos = c(1, 0))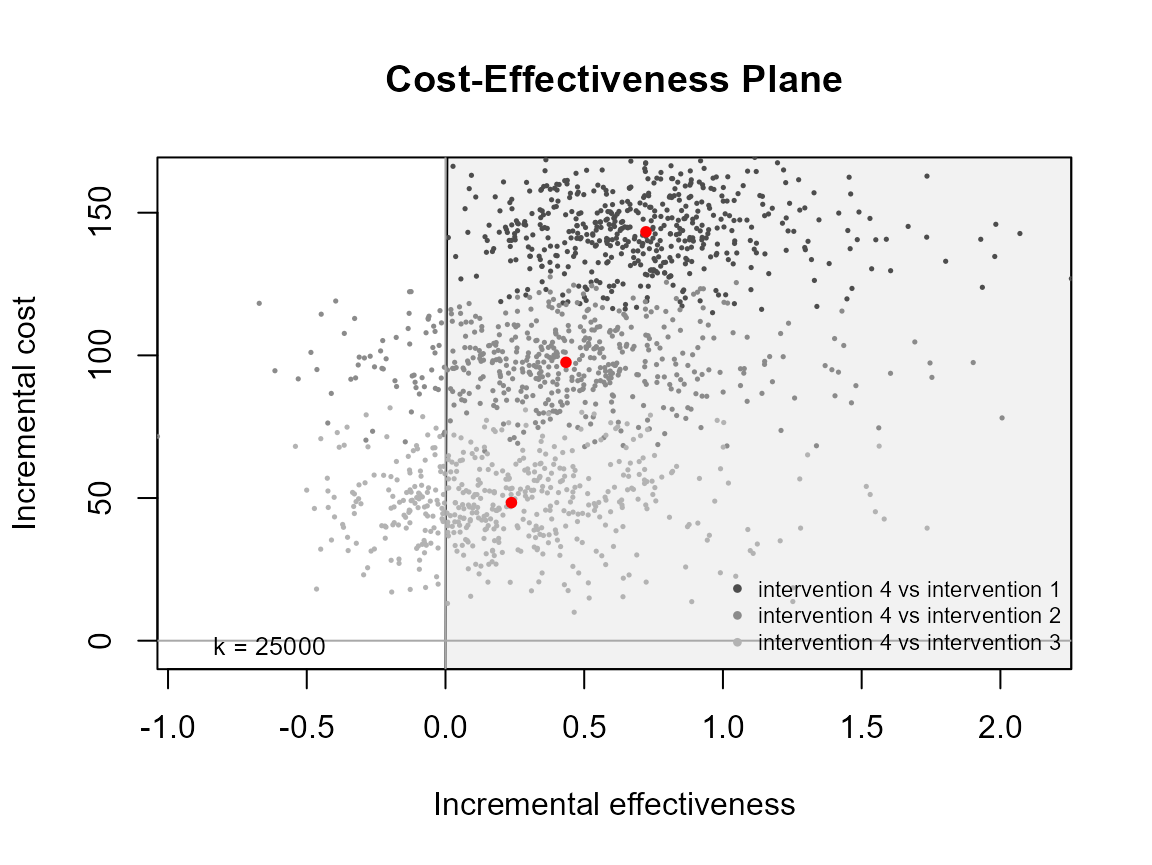
ceplane.plot(he, pos = c(1, 1))